The role of the board
It considers risk at the strategic level and defines the organisation’s appetite and approach to risk.
The board reviews risks, and identifies and monitors progress of the risk management plans.
The board will generally delegate these activities to a risk committee.
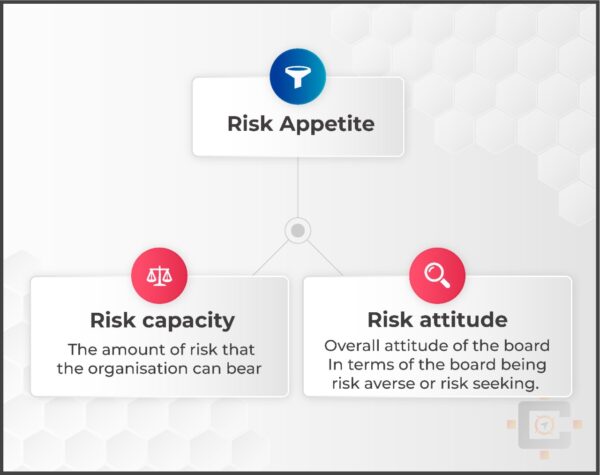
Risk Appetite
Risk appetite is the level of risk that an organization is prepared to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
It can be determined by:
- risk capacity – the amount of risk that the organisation can bear, and
- risk attitude – the overall character of the board, in terms of the board being risk averse or risk seeking.
Risk Management Committee
Risk Management Committee is the committee formed by board of directors to oversee the risk management policy and global risk management framework of the business.
Risk Management Committee will assist the Board of Directors in fulfilling its oversight responsibilities with regard to the risk appetite of the Corporation, the Corporation’s risk management.
It will have both NEDs and Executive directors also.

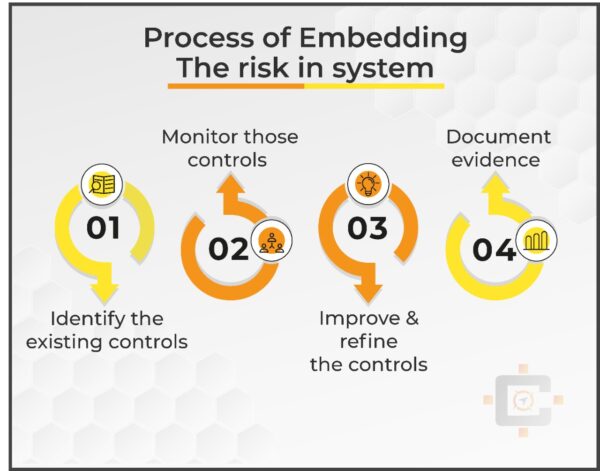
Embedding Risk in system
In reality, very few things happen which haven’t happened before. There will be an exception because we are living in an uncertain world.
So whatever bad things happened already in past, we should try that the same bad thing do not occur once again, so for that we need to do is that for each and every risk identified we must have controls in place which are effective.
And so this is called and embedding the risk in system.
Embedding the Risk in Culture
Embedding risk into culture and values therefore implies that risk management is ‘normal’ for the organisation. Risk management should become the behaviour of the organization.
An effective risk culture is one that enables and rewards individuals and groups for taking the right risks in an informed manner.
Risk Management: (TARA)
Transfer:
Risk can be transferred wholly or in part to a third party, so that if an adverse event occurs, the third party suffers all or most of the loss.
Avoid:
An organisation might choose to avoid a risk altogether.
However, since risks are unavoidable in business ventures, they can be avoided only by not investing.
Reduction/Mitigation:
Attempting to decrease the adverse effects should that risk actually crystallize.
There are various mitigation techniques like risk minimization, risk pooling & hedging techniques.
Accept:
Its’s simply accept that the risk may occur and decide to deal with the consequences in that particular situation. The strategy is appropriate normally where the adverse effect is minimal.

Risk Management: Diversification
Diversification can also help business to mitigate or reduce the overall risk they face.
Either your company can diversify through the different product or also diversify through entering new market.
By diversifying, the poor performance in one market can be set off by good performance in new market.

